Have you heard about Age-related Macular Degeneration (AMD)? It is a prevalent eye condition that affects the macula, the central part of the retina responsible for sharp, central vision. While AMD doesn't lead to complete blindness, it can significantly impair daily activities like reading, driving, and recognizing faces. Early detection and appropriate treatment are crucial in managing this condition. And in-order to do that you need to know enough about this condition and in this blog we will help you with a walk though.
Understanding Macular Degeneration
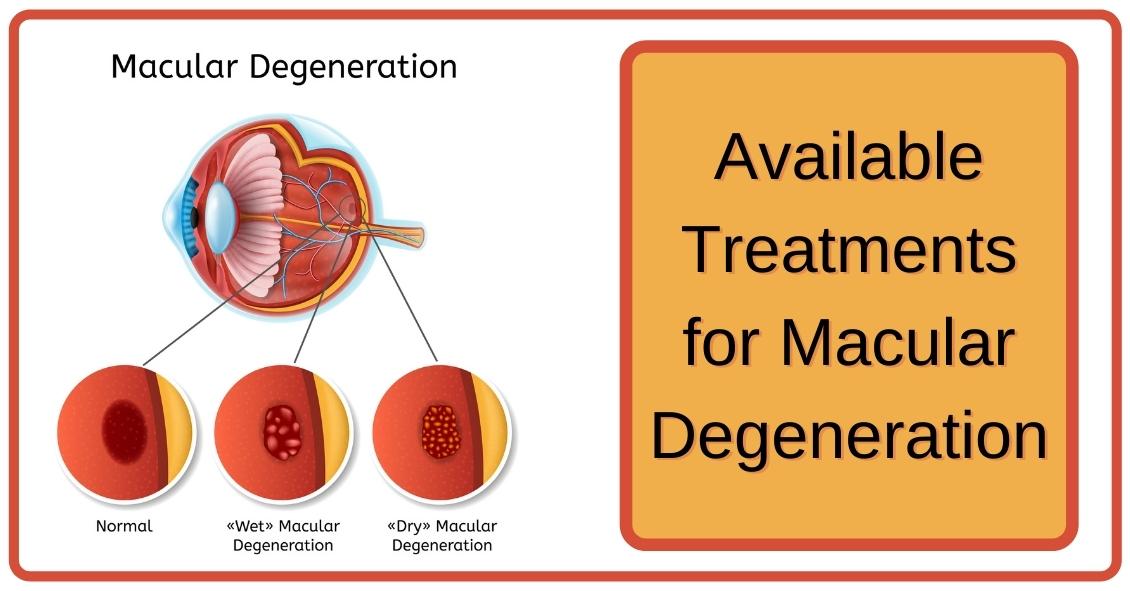
What Is AMD?
Age-related Macular Degeneration (AMD) majorly affects individuals over the age of 50 and causes the gradual deterioration of the macula, the central part of the retina responsible for sharp vision. This deterioration leads to blurred or distorted central vision, making everyday tasks like reading and recognizing faces more challenging. AMD can manifest in two main forms. Dry AMD is the more common type and occurs when the macula thins over time, causing a slow and progressive loss of central vision. On the other hand, Wet AMD is less common but more severe, involving the growth of abnormal blood vessels under the retina that leak fluid or blood, leading to rapid and significant vision loss
Symptoms of Macular Degeneration
In the early stages, AMD may not cause noticeable symptoms. As the condition progresses, symptoms may include:
- Blurred or distorted central vision
- Difficulty seeing in low light or when reading
- Dark or empty areas in the center of your vision
- Fading or changes in how you perceive colors
- Straight lines appearing wavy or bent
These symptoms typically affect both eyes but can start in one eye and gradually involve the other.
Treatment Options for Macular Degeneration
1. Lifestyle Modifications
For individuals with early-stage AMD, adopting a healthy lifestyle can help slow the progression:
- Diet:Consume a balanced diet rich in leafy greens, fruits, and fish high in omega-3 fattyacids.
- Supplements: The Age-Related Eye Disease Study 2 (AREDS2) formula, which includes vitamins C and E, zinc, copper, lutein, and zeaxanthin, may reduce the risk ofprogression in intermediate or advanced AMD.
- Exercise: Regular physical activity can improve overall eye health.
- Smoking Cessation: Avoiding smoking can significantly reduce the risk of developing AMD.
2. Medical Treatments for Wet AMD
Wet AMD requires more aggressive treatment to prevent rapid vision loss:
- Anti-VEGF Injections: Medications like Lucentis (ranibizumab), Eylea (aflibercept), and Beovu (brolucizumab) are injected into the eye to inhibit the growth of abnormal blood vessels and reduce fluid leakage.
- Photodynamic Therapy (PDT): This treatment involves injecting a light-sensitive drug into the bloodstream, which is then activated by a laser to destroy abnormal blood vessels in the retina
- Laser Therapy: In some cases, a laser is used to directly destroy abnormal blood vessels.
3. Supportive Treatments for Dry AMD
While there's no cure for dry AMD, certain measures can help manage the condition:
- Low Vision Aids: Devices like magnifying glasses, large-print books, and screen readers can assist in daily activities.
- Low Vision Rehabilitation: Specialized training can help individuals adapt to vision changes and maintain independence.
- Surgical Options: In advanced cases, surgical implantation of a telescopic lens can improve vision by magnifying images.
Emerging Treatments and Research
Advancements in medical research are leading to new treatment options:
- Gene Therapy: Researchers are exploring gene therapy as a potential treatment for AMD, aiming to address the underlying causes of the disease.
- Avacincaptad Pegol (Izervay): Approved in 2023, this complement inhibitor targets geographic atrophy, a form of dry AMD, by reducing inflammation and slowing disease progression.
- Bionic Telescope Implants:These devices are surgically implanted to assist individuals with severe vision loss due to AMD, helping them see objects more clearly.
Preventive Measures and Eye Health Tips
While some risk factors like age and genetics cannot be controlled, adopting a healthy lifestyle can reduce the risk of developing AMD:
Regular Eye Exams: Routine check-ups can help detect AMD in its early stages. Early detection allows timely intervention, which can slow the progression of the disease. Eye exams also help monitor overall eye health and identify other vision problems before they worsen.
Healthy Diet: Incorporate foods rich in antioxidants, such as leafy greens, nuts, and fish. These nutrients help protect the retina from oxidative stress and damage. A balanced diet also supports overall eye health and can reduce the risk of other age-related eye conditions.
Protective Eyewear: Wear sunglasses that block UV rays to protect the eyes from harmful light. UV protection helps prevent damage to the macula and reduces the risk of cataracts. Additionally, wearing protective eyewear outdoors can shield your eyes from dust and other environmental irritants.
Avoid Smoking: Smoking increases the risk of AMD and accelerates its progression. Chemicals in cigarettes can damage blood vessels in the eyes, worsening vision loss. Quitting smoking also improves overall circulation and supports long-term eye health.
Conclusion
Macular Degeneration is a serious eye condition that can impact quality of life. However, with early detection, appropriate medical treatments, and lifestyle modifications, its progression can be managed effectively. If you experience any symptoms associated with AMD, consult an eye care professional promptly. Regular eye exams and a proactive approach to eye health are essential in preserving vision.
Book Appointment